Flutter + Kotlin Multiplatform, Write Once Run Anywhere
Motivation
Flutter是Google 2017年推出的跨平台框架,拥有Fast Development,Expressive and Flexible UI,Native Performance等特点。Flutter使用Dart作为开发语言,Android和iOS项目可以共用一套Dart代码,很多人迫不及待的尝试,包括我,但在学习的过程中,同时在思考以下的问题:
-
Flutter很优秀,但相对来说还比较新,目前并不是所有的第三方SDK支持Flutter(特别是在国内),所以在使用第三方SDK时很多时候需要我们编写原生代码集成逻辑,需要Android和iOS分别编写不同的集成代码。
-
项目要集成Flutter,一次性替换所有页面有点不太实际,但是部分页面集成的时候,会面临需要将数据库操作等公用逻辑使用Dart重写一遍的问题,因为原生的逻辑在其他的页面也需要用到,没办法做到只保留Dart的实现代码,所以很容易出现一套逻辑需要提供不同平台的实现如:
Dao.kt,Dao.swift,Dao.dart。当然可以使用Flutter提供的MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel来直接调用原生代码的逻辑,但是如果数据库操作逻辑需要修改的时候,我们依然要同时修改不同平台的代码逻辑。 -
项目组里有內部的SDK,同时提供给不同项目(Android和iOS)使用,但是一些App需要集成Flutter,就需要SDK分别提供Flutter/Android/iOS的代码实现,这时需要同时维护三个SDK反而增加了SDK维护者的维护和实现成本。
所以,最后可以把问题归结为原生代码无法复用,导致我们需要为不同平台提供同一代码逻辑实现。那么有没有能让原生代码复用的框架,答案是肯定的,Kotlin Multiplatform是Kotlin的一个功能(目前还在实验性阶段),其目标就是使用Kotlin:Sharing code between platforms。
于是我有一个大胆的想法,同时使用Flutter和Kotlin Multiplatform,虽然使用不同的语言(Dart/Kotlin),但不同平台共用一套代码逻辑实现。使用Kotlin Multiplatform编写公用逻辑,然后在Android/iOS上使用MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel供Flutter调用公用逻辑。
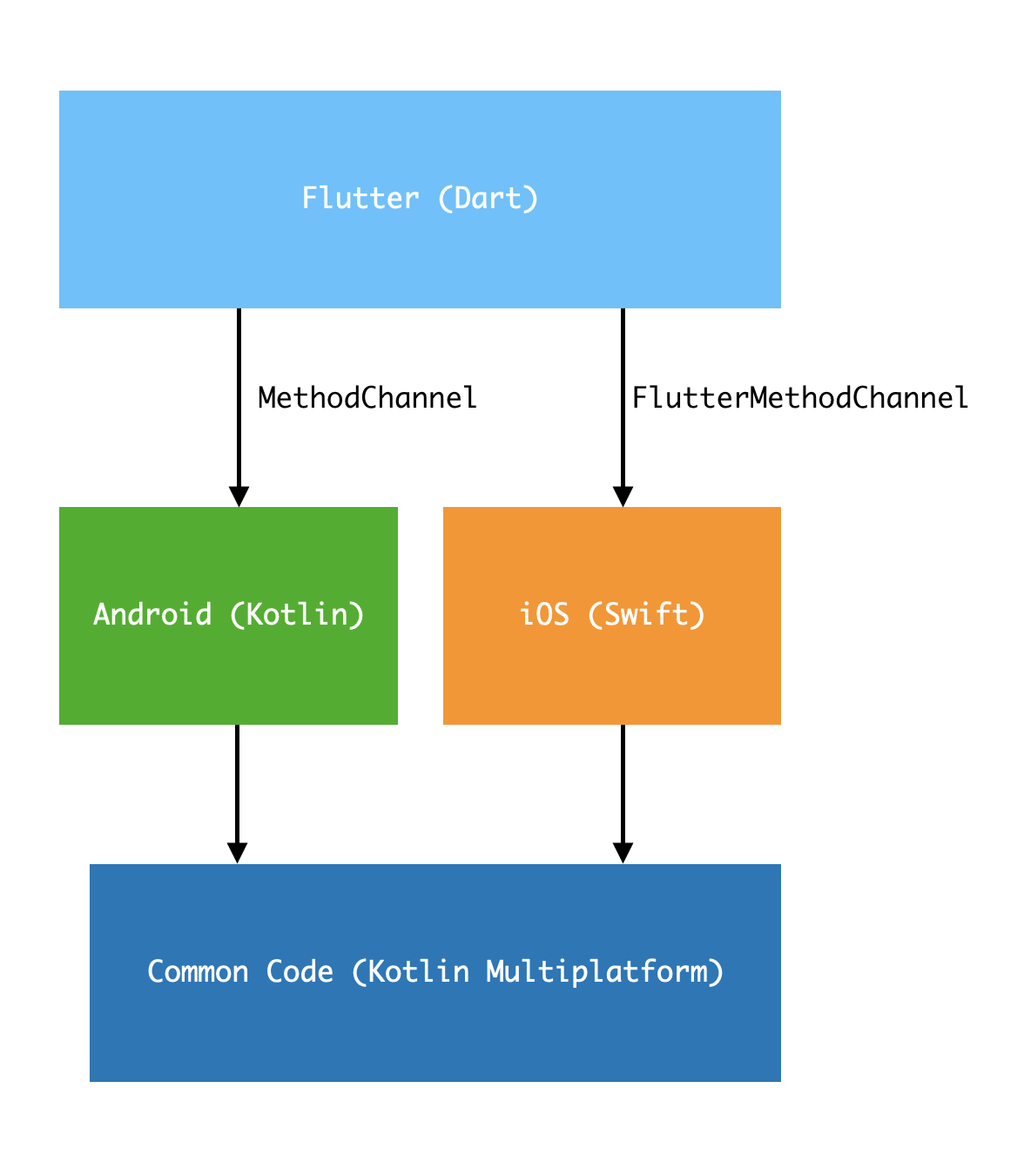
接下来以实现公用的数据库操作逻辑为例,来简单描述如何使用Flutter和Kotlin Multiplatform达到Write Once Run Anywhere。
接下来的内容需要读者对Flutter和Kotlin Multiplatform有所了解。
Kotlin Multiplatform
我们使用Sqldelight实现公用的数据库操作逻辑,然后通过kotlinx.serialization把查询结果序列化为json字符串,通过MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel传递到Flutter中使用。
Flutter的目录结构如下面所示:
|
|__android
| |__app
|__ios
|__lib
|__test
其中android目录下是一个完整的Gradle项目,参照官方文档Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android,我们在android目录下创建一个common module,来存放公用的代码逻辑。
Gradle脚本
apply plugin: 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.multiplatform'
apply plugin: 'com.squareup.sqldelight'
apply plugin: 'kotlinx-serialization'
sqldelight {
AccountingDB {
packageName = "com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform"
}
}
kotlin {
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.common
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.common
}
androidMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.sqldelight.runtimejvm
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.runtime
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.android
}
iosMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.sqldelight.driver.ios
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.native
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.native
}
}
targets {
fromPreset(presets.jvm, 'android')
final def iOSTarget = System.getenv('SDK_NAME')?.startsWith("iphoneos") \
? presets.iosArm64 : presets.iosX64
fromPreset(iOSTarget, 'ios') {
binaries {
framework('common')
}
}
}
}
// workaround for https://youtrack.jetbrains.com/issue/KT-27170
configurations {
compileClasspath
}
task packForXCode(type: Sync) {
final File frameworkDir = new File(buildDir, "xcode-frameworks")
final String mode = project.findProperty("XCODE_CONFIGURATION")?.toUpperCase() ?: 'DEBUG'
final def framework = kotlin.targets.ios.binaries.getFramework("common", mode)
inputs.property "mode", mode
dependsOn framework.linkTask
from { framework.outputFile.parentFile }
into frameworkDir
doLast {
new File(frameworkDir, 'gradlew').with {
text = "#!/bin/bash\nexport 'JAVA_HOME=${System.getProperty("java.home")}'\ncd '${rootProject.rootDir}'\n./gradlew \$@\n"
setExecutable(true)
}
}
}
tasks.build.dependsOn packForXCode
实现AccountingRepository
在common module下创建commonMain目录,并在commonMain目录下创建AccountingRepository类用于封装数据库操作逻辑(这里不需要关心代码实现细节,只是简单的查询数据库结果,然后序列化为json字符串)。
class AccountingRepository(private val accountingDB: AccountingDB) {
private val json: Json by lazy {
Json(JsonConfiguration.Stable)
}
...
fun getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonthList: List<String>): String {
val list = mutableListOf<GetMonthTotalAmount>()
.apply {
for (yearAndMonth in yearAndMonthList) {
val r = accountingDB.accountingDBQueries
.getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
.executeAsOneOrNull()
if (r?.total != null && r.yearMonth != null) {
add(r)
}
}
}
.map {
it.toGetMonthTotalAmountSerialization()
}
return json.stringify(GetMonthTotalAmountSerialization.serializer().list, list)
}
fun getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth: String): String {
val list = accountingDB.accountingDBQueries
.getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
.executeAsList()
.map {
it.toGetGroupingMonthTotalAmountSerialization()
}
return json.stringify(GetGroupingMonthTotalAmountSerialization.serializer().list, list)
}
}
到这里我们已经实现了公用的数据库操作逻辑,但是为了Android/iOS更加简单的调用数据库操作逻辑,我们把MethodChannel#setMethodCallHandler/FlutterMethodChannel#setMethodCallHandler中的调用逻辑进行简单的封装:
const val SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL = "com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform/sqldelight"
class SqlDelightManager(
private val accountingRepository: AccountingRepository
) : CoroutineScope {
...
fun methodCall(method: String, arguments: Map<String, Any>, result: (Any) -> Unit) {
launch(coroutineContext) {
when (method) {
...
"getMonthTotalAmount" -> {
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST") val yearAndMonthList: List<String> =
arguments["yearAndMonthList"] as? List<String> ?: emptyList()
val r = accountingRepository.getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonthList)
result(r)
}
"getGroupingMonthTotalAmount" -> {
val yearAndMonth: String = arguments["yearAndMonth"] as? String ?: ""
val r = accountingRepository.getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
result(r)
}
}
}
}
}
因为MethodChannel#setMethodHandler中Result和FlutterMethodChannel#setMethodHandler中FlutterResult对象不一样,所以我们在SqlDelightManager#methodCall定义result function以回调的形式让外部处理。
在Android使用SqlDelightManager
在Android项目使用SqlDelightManager,参考官方文档Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android,我们需要先在app目录下添加对common module的依赖:
implementation project(":common")
参照官方文档Writing custom platform-specific code,我们在MainActivity实现MethodChannel并调用SqlDelightManager#methodCall:
class MainActivity: FlutterActivity() {
private val sqlDelightManager by lazy {
val accountingRepository = AccountingRepository(Db.getInstance(applicationContext))
SqlDelightManager(accountingRepository)
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.registerWith(this)
MethodChannel(flutterView, SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler { methodCall, result ->
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
val args = methodCall.arguments as? Map<String, Any> ?: emptyMap()
sqlDelightManager.methodCall(methodCall.method, args) {
result.success(it)
}
}
}
...
}
在iOS使用SqlDelightManager
继续参考Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android,让Xcode项目识别common module的代码,主要把common module生成的frameworks添加Xcode项目中,我简单总结为以下步骤:
- 运行
./gradlew :common:build,生成iOS frameworks - General -> 添加Embedded Binaries
- Build Setting -> 添加Framework Search Paths
- Build Phases -> 添加Run Script
有一点跟官方文档不同的是,frameworks的存放目录不一样,因为Flutter项目结构把android项目的build文件路径放到根目录,所以frameworks的路径应该是$(SRCROOT)/../build/xcode-frameworks。可以查看android/build.gradle:
rootProject.buildDir = '../build'
subprojects {
project.buildDir = "${rootProject.buildDir}/${project.name}"
}
这几步完成之后就可以在Swift里面调用common module的Kotlin代码了。参照官方文档Writing custom platform-specific code,我们在AppDelegate.swift实现FlutterMethodChannel并调用SqlDelightManager#methodCall(Swift代码全是靠Google搜出来的XD):
@UIApplicationMain
@objc class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
lazy var sqlDelightManager: SqlDelightManager = {
Db().defaultDriver()
let accountingRepository = AccountingRepository(accountingDB: Db().instance)
return SqlDelightManager(accountingRepository: accountingRepository)
}()
override func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
) -> Bool {
let controller: FlutterViewController = window?.rootViewController as! FlutterViewController
let sqlDelightChannel = FlutterMethodChannel(
name: SqlDelightManagerKt.SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL,
binaryMessenger: controller)
sqlDelightChannel.setMethodCallHandler({
[weak self] (methodCall: FlutterMethodCall, flutterResult: @escaping FlutterResult) -> Void in
let args = methodCall.arguments as? [String: Any] ?? [:]
self?.sqlDelightManager.methodCall(
method: methodCall.method,
arguments: args,
result: {(r: Any) -> KotlinUnit in
flutterResult(r)
return KotlinUnit()
})
})
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: self)
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)
}
...
}
可以看到,除了MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel对象不同以及Kotlin/Swift语法不同,我们调用的是同一方法SqlDelightManager#methodCall,并不需要分别在Android/iOS上实现同一套逻辑。
到这里我们已经使用了Kotlin Multiplatform实现原生代码复用了,然后我们只需在Flutter使用MethodChannel调用相应的方法就可以了。
Flutter
同样的我们在Flutter中也实现AccountingRepository类封装数据库操作逻辑:
class AccountingRepository {
static const _platform =
const MethodChannel("com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform/sqldelight");
...
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfMonth>> getMonthTotalAmount(
[DateTime latestMonth]) async {
var dateTime = latestMonth ?? DateTime.now();
var yearMonthList = List<String>();
for (var i = 0; i <= 6; i++) {
var d = DateTime(dateTime.year, dateTime.month - i, 1);
yearMonthList.add(_yearMonthFormat.format(d));
}
var arguments = {"yearAndMonthList": yearMonthList};
var result = await _platform.invokeMethod("getMonthTotalAmount", arguments);
return deserializeListOf<TotalExpensesOfMonth>(jsonDecode(result));
}
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>> getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth(
DateTime latestMonth) async {
return getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(latestMonth);
}
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>> getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(
DateTime dateTime) async {
var arguments = {"yearAndMonth": _yearMonthFormat.format(dateTime)};
var result =
await _platform.invokeMethod("getGroupingMonthTotalAmount", arguments);
return deserializeListOf<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>(jsonDecode(result));
}
}
简单使用BLoC来调用AccountingRepository的方法:
class SummaryBloc {
SummaryBloc(this._db);
final AccountingRepository _db;
final _summaryChartDataSubject =
BehaviorSubject<SummaryChartData>.seeded(...);
final _summaryListSubject =
BehaviorSubject<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>>.seeded(BuiltList());
Stream<SummaryChartData> get summaryChartData =>
_summaryChartDataSubject.stream;
Stream<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>> get summaryList =>
_summaryListSubject.stream;
...
Future<Null> getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth({DateTime dateTime}) async {
var list =
await _db.getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth(dateTime ?? DateTime.now());
_summaryListSubject.sink.add(_createSummaryList(list));
}
Future<Null> getMonthTotalAmount({DateTime dateTime}) async {
...
var result = await _db.getMonthTotalAmount(dateTime);
...
_summaryChartDataSubject.sink.add(...);
}
...
在Widget中使用BLoC:
class SummaryPage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _SummaryPageState();
}
class _SummaryPageState extends State<SummaryPage> {
final _summaryBloc = SummaryBloc(AccountingRepository.db);
...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
...
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Divider(
height: 1.0,
),
Container(
color: Colors.white,
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 10),
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: _summaryBloc.summaryChartData,
builder: (BuildContext context,
AsyncSnapshot<SummaryChartData> snapshot) {
...
},
),
),
Expanded(
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: _summaryBloc.summaryList,
builder: (BuildContext context,
AsyncSnapshot<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>> snapshot) {
...
},
),
)
],
),
);
}
}
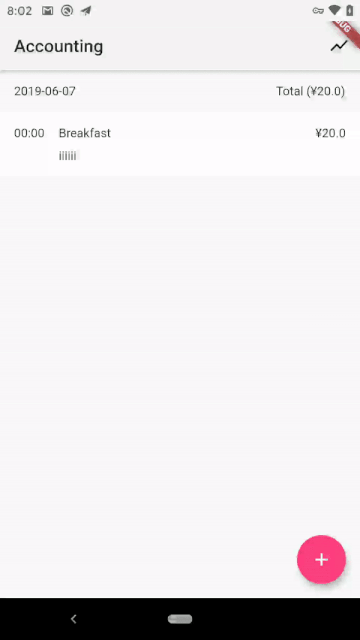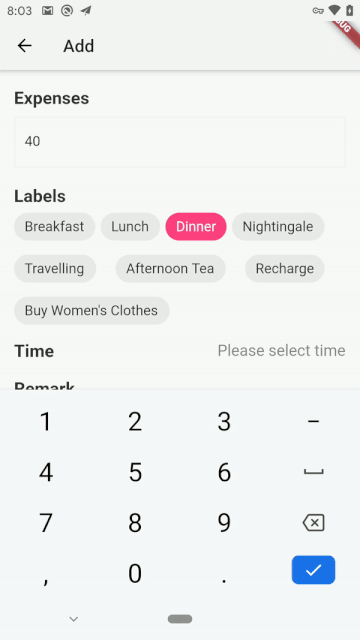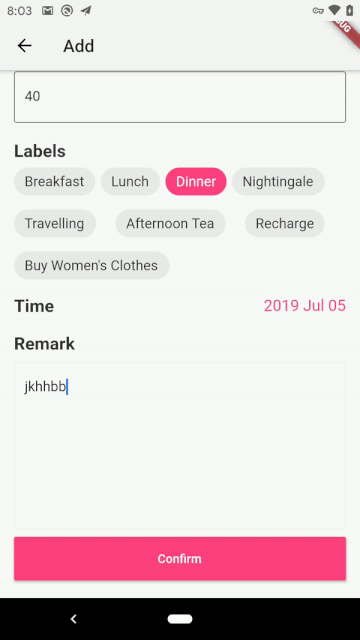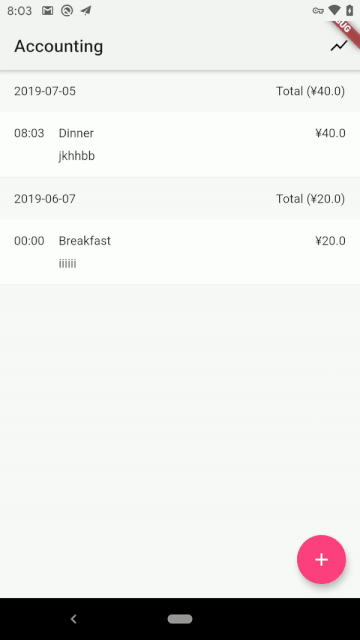
完结撒花,最后我们来看看项目的运行效果:
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Unit Test
为了保证代码质量和逻辑正确性Unit Test是必不可少的,对于common module代码,我们只要在commonTest中写一套Unit Test就可以了,当然有时候我们需要为不同平台编写不同的测试用例。在Demo里我主要使用MockK来mock数据,但是遇到一些问题,在Kotlin/Native无法识别MockK的引用。对于这个问题,我提了一个issue,目前还在处理中。
TL;DR
跨平台这个话题在现在已经是老生常谈了,很多公司很多团队都希望使用跨平台技术来提高开发效率,降低人力成本,但开发的过程中会发现踩的坑越来越多,很多时候并没有达到当初的预期,个人认为跨平台的最大目标是代码复用,Write Once Run Anywhere,让多端的开发者共同实现和维护同一代码逻辑,减少沟通导致实现的差异和多端代码实现导致的差异,使代码更加健壮便于维护。
本文简单演示了如何使用Flutter和Kotlin Multiplatform来达到Write Once Run Anywhere的效果。个人认为Kotlin Multiplatform有很大的前景,Kotlin Multiplatform还支持JS平台,所以公用的代码理论上还能提供给小程序使用(希望有机会验证这个猜想)。在今年的Google IO上Google发布了下一代UI开发框架Jetpack Compose,苹果开发者大会上苹果为我们带来了SwiftUI,这意味着如果把这2个框架的API统一起来,我们可以使用Kotlin来编写拥有Native性能的跨平台的代码。Demo已经上传到github,感兴趣的可以clone下来研究(虽然写的很烂)。有问题可以在github上提issue。Have Fun!