Flutter + Kotlin Multiplatform, Write Once Run Anywhere [EN]
Motivation
Flutter is a Google’s cross-platform framework launched in 2017, featuring Fast Development, Expressive and Flexible UI, Native Performance and more. Flutter uses Dart as the development language, Android and iOS projects can share the same Dart code. Many people can’t wait to try it, including me, but during the learning process, I am thinking about the following questions:
-
Flutter is excellent, but relatively new. At present, not all third-party SDKs support Flutter (especially in China), when using third-party SDKs, we often need to write native code integration logic, which requires us to write separate integration code for Android and iOS separately.
-
When we want to integrate Flutter into our project, it is a bit impractical to replace all the pages at once, but when we need some pages integration, we will need to use Dart for rewriting the common logic such as database operations logic. Because other pages also need using database operation logic, there is no way to keep only Dart’s implementation code. Thus, the same database operation logic will need to provide different frameworks implementations such as:
Dao.kt,Dao.swift,Dao.dart. Of course, you can use theMethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannelprovided by Flutter to directly call the logic of the native code, but if the database operation logic needs to be modified, we still have to modify the code logic of the different frameworks at the same time. -
If your team has an internal SDK that is available for different projects (Android and iOS), but some APPs need to integrate Flutter, the maintainer will need to provide the Flutter/Android/iOS SDK separately which increases the maintenance and implementation costs of the SDK maintainer.
Therefore, the problem can be attributed to the fact that native code cannot be reused, which leads us to implement the same code logic for different frameworks. Is there any frameworks for reusing native code? Definitely YES! Kotlin Multiplatform is a feature of Kotlin (currently experimental) with the goal of using Kotlin: Sharing code between platforms.
Hence, I have a bold idea to use both Flutter and Kotlin Multiplatform, although different languages (Dart/Kotlin) are used, different frameworks share the same code logic implementations. Write common logic using Kotlin Multiplatform, then use MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel on Android/iOS for Flutter to call the common logic.
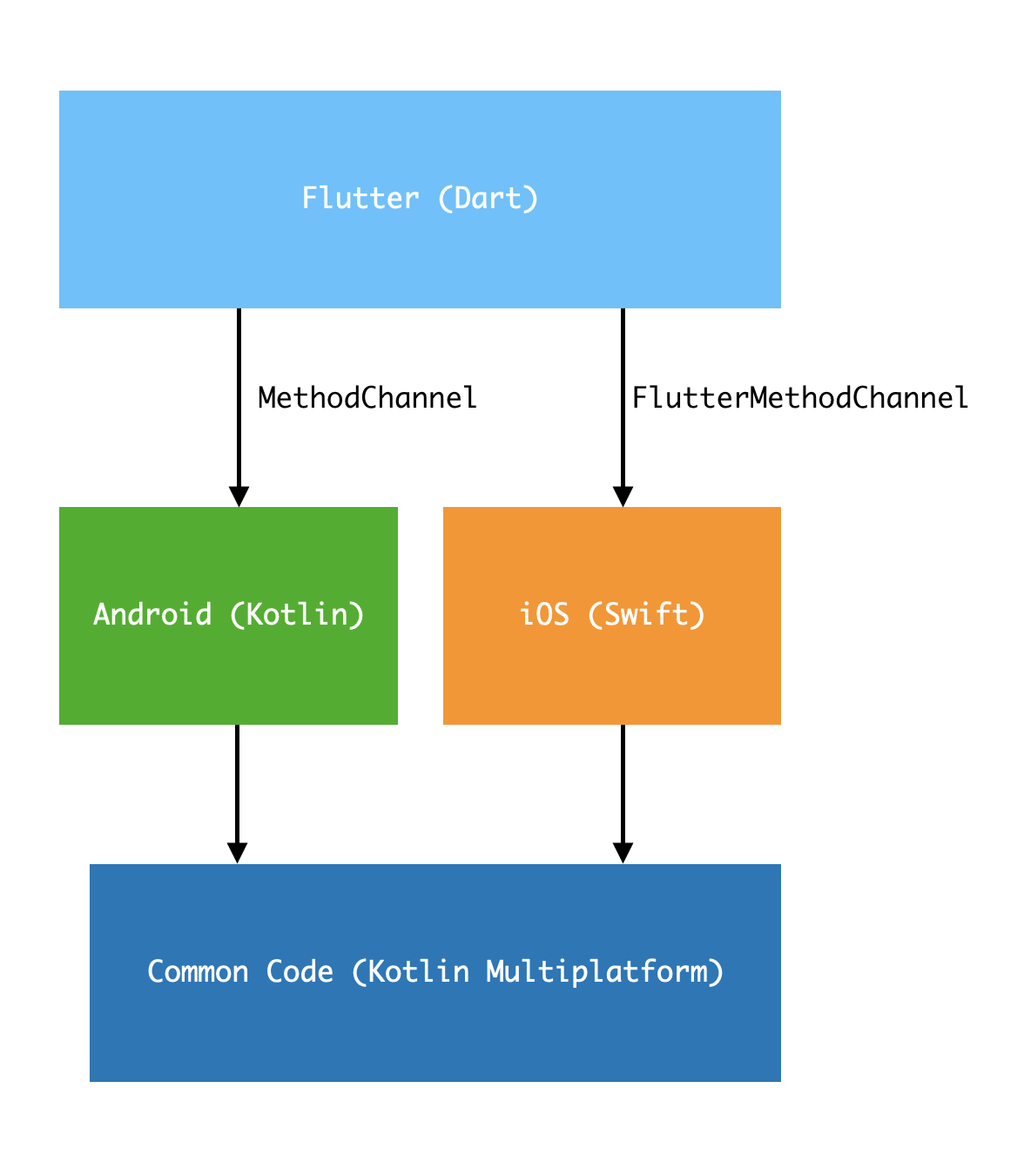
Let’s take an example of implementing common database logic and briefly describe how to achieve the goal of Write Once Run Anywhere using Flutter and Kotlin Multiplatform.
Kotlin Multiplatform
We use Sqldelight to implement common database logic, then serialize the query results into json strings via kotlinx.serialization and pass them to Flutter via MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel.
The project structure of Flutter is shown as below:
|
|__android
| |__app
|__ios
|__lib
|__test
The android directory is a Gradle project, refer to the official document Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android, we create a common module in the android directory to store the common logic code.
Gradle script
apply plugin: 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.multiplatform'
apply plugin: 'com.squareup.sqldelight'
apply plugin: 'kotlinx-serialization'
sqldelight {
AccountingDB {
packageName = "com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform"
}
}
kotlin {
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.common
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.common
}
androidMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.sqldelight.runtimejvm
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.runtime
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.android
}
iosMain.dependencies {
implementation deps.kotlin.stdlib.stdlib
implementation deps.sqldelight.driver.ios
implementation deps.kotlin.serialiaztion.runtime.native
implementation deps.kotlin.coroutines.native
}
}
targets {
fromPreset(presets.jvm, 'android')
final def iOSTarget = System.getenv('SDK_NAME')?.startsWith("iphoneos") \
? presets.iosArm64 : presets.iosX64
fromPreset(iOSTarget, 'ios') {
binaries {
framework('common')
}
}
}
}
// workaround for https://youtrack.jetbrains.com/issue/KT-27170
configurations {
compileClasspath
}
task packForXCode(type: Sync) {
final File frameworkDir = new File(buildDir, "xcode-frameworks")
final String mode = project.findProperty("XCODE_CONFIGURATION")?.toUpperCase() ?: 'DEBUG'
final def framework = kotlin.targets.ios.binaries.getFramework("common", mode)
inputs.property "mode", mode
dependsOn framework.linkTask
from { framework.outputFile.parentFile }
into frameworkDir
doLast {
new File(frameworkDir, 'gradlew').with {
text = "#!/bin/bash\nexport 'JAVA_HOME=${System.getProperty("java.home")}'\ncd '${rootProject.rootDir}'\n./gradlew \$@\n"
setExecutable(true)
}
}
}
tasks.build.dependsOn packForXCode
Implement AccountingRepository
Create the commonMain directory under the common module, and create the AccountingRepository class in the commonMain directory to encapsulate the database logic (you don’t need to care about the code implementation details here, the logic here is simply querying the database results and then serializing them to json strings).
class AccountingRepository(private val accountingDB: AccountingDB) {
private val json: Json by lazy {
Json(JsonConfiguration.Stable)
}
...
fun getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonthList: List<String>): String {
val list = mutableListOf<GetMonthTotalAmount>()
.apply {
for (yearAndMonth in yearAndMonthList) {
val r = accountingDB.accountingDBQueries
.getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
.executeAsOneOrNull()
if (r?.total != null && r.yearMonth != null) {
add(r)
}
}
}
.map {
it.toGetMonthTotalAmountSerialization()
}
return json.stringify(GetMonthTotalAmountSerialization.serializer().list, list)
}
fun getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth: String): String {
val list = accountingDB.accountingDBQueries
.getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
.executeAsList()
.map {
it.toGetGroupingMonthTotalAmountSerialization()
}
return json.stringify(GetGroupingMonthTotalAmountSerialization.serializer().list, list)
}
}
We have implemented the common database logic here, but for Android/iOS to call the database logic more simply, we simply encapsulate the call logic of MethodChannel#setMethodCallHandler/FlutterMethodChannel#setMethodCallHandler:
const val SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL = "com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform/sqldelight"
class SqlDelightManager(
private val accountingRepository: AccountingRepository
) : CoroutineScope {
...
fun methodCall(method: String, arguments: Map<String, Any>, result: (Any) -> Unit) {
launch(coroutineContext) {
when (method) {
...
"getMonthTotalAmount" -> {
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST") val yearAndMonthList: List<String> =
arguments["yearAndMonthList"] as? List<String> ?: emptyList()
val r = accountingRepository.getMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonthList)
result(r)
}
"getGroupingMonthTotalAmount" -> {
val yearAndMonth: String = arguments["yearAndMonth"] as? String ?: ""
val r = accountingRepository.getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(yearAndMonth)
result(r)
}
}
}
}
}
Because the Result object in MethodChannel#setMethodHandler is different from the FlutterResult object in FlutterMethodChannel#setMethodHandler, we define the result function in SqlDelightManager#methodCall as external processing in the form of callbacks.
Use SqlDelightManager on Android
In order to use SqlDelightManager in Android projects, refer to the official documentation Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android, we need to add the dependency of common module to the app module firstly:
implementation project(":common")
Referring to the official document Writing custom platform-specific code, we implement the MethodChannel in the MainActivity and call the SqlDelightManager#methodCall function:
class MainActivity: FlutterActivity() {
private val sqlDelightManager by lazy {
val accountingRepository = AccountingRepository(Db.getInstance(applicationContext))
SqlDelightManager(accountingRepository)
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.registerWith(this)
MethodChannel(flutterView, SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler { methodCall, result ->
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
val args = methodCall.arguments as? Map<String, Any> ?: emptyMap()
sqlDelightManager.methodCall(methodCall.method, args) {
result.success(it)
}
}
}
...
}
Use SqlDelightManager on iOS
Referring to the Multiplatform Project: iOS and Android. In order for the Xcode project to recognize the code of the common module, you need to add the frameworks generated by the common module to the Xcode project. I briefly summarize the following steps:
- Run
./gradlew :common:buildto generate the iOS frameworks - General -> Add Embedded Binaries
- Build Setting -> Add Framework Search Paths
- Build Phases -> Add Run Script
The only different from the official documentation is that the path to store frameworks is different. Because the Flutter project structure puts the build path of the android project to the root directory, the path of the frameworks should be $(SRCROOT)/../build/xcode- frameworks. You can check it in android/build.gradle:
rootProject.buildDir = '../build'
subprojects {
project.buildDir = "${rootProject.buildDir}/${project.name}"
}
Afterwards, you can call the Kotlin code of the common module in Swift. Referring to the official documentation, Writing custom platform-specific code, we implement the FlutterMethodChannel in AppDelegate.swift and call the SqlDelightManager#methodCall function:
@UIApplicationMain
@objc class AppDelegate: FlutterAppDelegate {
lazy var sqlDelightManager: SqlDelightManager = {
Db().defaultDriver()
let accountingRepository = AccountingRepository(accountingDB: Db().instance)
return SqlDelightManager(accountingRepository: accountingRepository)
}()
override func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
) -> Bool {
let controller: FlutterViewController = window?.rootViewController as! FlutterViewController
let sqlDelightChannel = FlutterMethodChannel(
name: SqlDelightManagerKt.SQLDELIGHT_CHANNEL,
binaryMessenger: controller)
sqlDelightChannel.setMethodCallHandler({
[weak self] (methodCall: FlutterMethodCall, flutterResult: @escaping FlutterResult) -> Void in
let args = methodCall.arguments as? [String: Any] ?? [:]
self?.sqlDelightManager.methodCall(
method: methodCall.method,
arguments: args,
result: {(r: Any) -> KotlinUnit in
flutterResult(r)
return KotlinUnit()
})
})
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.register(with: self)
return super.application(application, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: launchOptions)
}
...
}
As you can see, except for the MethodChannel/FlutterMethodChannel object and the Kotlin/Swift syntax, we are calling the same SqlDelightManager#methodCall function and don’t need to implement the same logic on Android/iOS.
Finally, we have used Kotlin Multiplatform to reuse the native code. The only thing is to use MethodChannel to call the corresponding method in Flutter.
Flutter
Similarly, we implement the AccountingRepository class to encapsulate database logic in Flutter:
class AccountingRepository {
static const _platform =
const MethodChannel("com.littlegnal.accountingmultiplatform/sqldelight");
...
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfMonth>> getMonthTotalAmount(
[DateTime latestMonth]) async {
var dateTime = latestMonth ?? DateTime.now();
var yearMonthList = List<String>();
for (var i = 0; i <= 6; i++) {
var d = DateTime(dateTime.year, dateTime.month - i, 1);
yearMonthList.add(_yearMonthFormat.format(d));
}
var arguments = {"yearAndMonthList": yearMonthList};
var result = await _platform.invokeMethod("getMonthTotalAmount", arguments);
return deserializeListOf<TotalExpensesOfMonth>(jsonDecode(result));
}
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>> getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth(
DateTime latestMonth) async {
return getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(latestMonth);
}
Future<BuiltList<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>> getGroupingMonthTotalAmount(
DateTime dateTime) async {
var arguments = {"yearAndMonth": _yearMonthFormat.format(dateTime)};
var result =
await _platform.invokeMethod("getGroupingMonthTotalAmount", arguments);
return deserializeListOf<TotalExpensesOfGroupingTag>(jsonDecode(result));
}
}
Simply use BLoC to call the AccountingRepository functions:
class SummaryBloc {
SummaryBloc(this._db);
final AccountingRepository _db;
final _summaryChartDataSubject =
BehaviorSubject<SummaryChartData>.seeded(...);
final _summaryListSubject =
BehaviorSubject<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>>.seeded(BuiltList());
Stream<SummaryChartData> get summaryChartData =>
_summaryChartDataSubject.stream;
Stream<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>> get summaryList =>
_summaryListSubject.stream;
...
Future<Null> getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth({DateTime dateTime}) async {
var list =
await _db.getGroupingTagOfLatestMonth(dateTime ?? DateTime.now());
_summaryListSubject.sink.add(_createSummaryList(list));
}
Future<Null> getMonthTotalAmount({DateTime dateTime}) async {
...
var result = await _db.getMonthTotalAmount(dateTime);
...
_summaryChartDataSubject.sink.add(...);
}
...
Use BLoC in Widgets:
class SummaryPage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() => _SummaryPageState();
}
class _SummaryPageState extends State<SummaryPage> {
final _summaryBloc = SummaryBloc(AccountingRepository.db);
...
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
...
body: Column(
children: <Widget>[
Divider(
height: 1.0,
),
Container(
color: Colors.white,
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 10),
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: _summaryBloc.summaryChartData,
builder: (BuildContext context,
AsyncSnapshot<SummaryChartData> snapshot) {
...
},
),
),
Expanded(
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: _summaryBloc.summaryList,
builder: (BuildContext context,
AsyncSnapshot<BuiltList<SummaryListItem>> snapshot) {
...
},
),
)
],
),
);
}
}
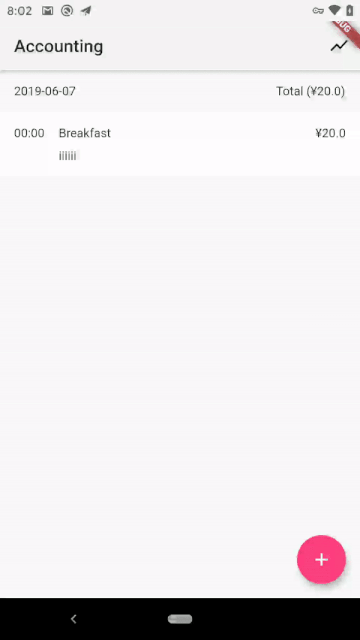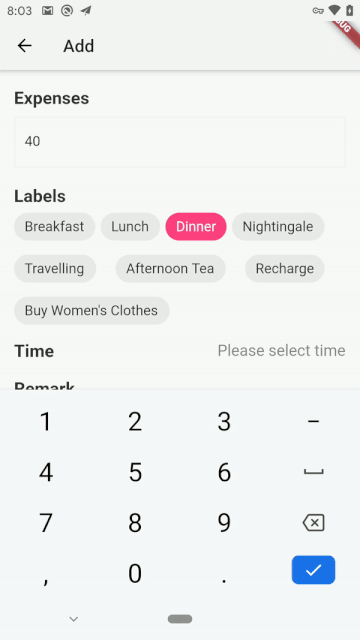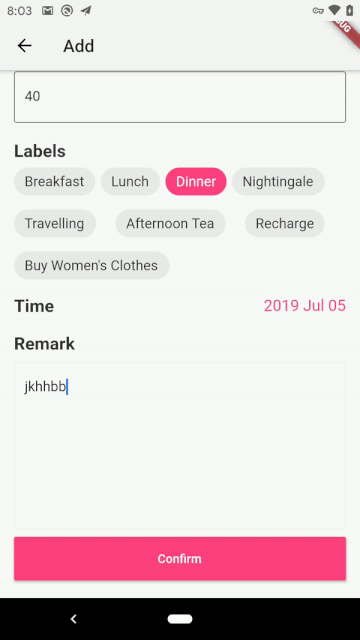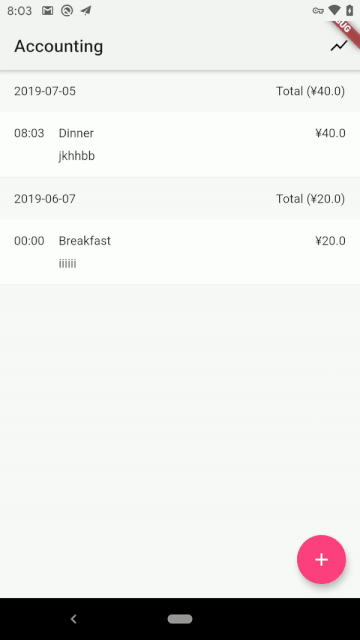
DONE! Let’s take a look at what the APP looks like:
| Android | iOS |
|---|---|
 |
 |
TL;DR
This article briefly demonstrates how to use both Flutter and Kotlin Multiplatform to achieve Write Once Run Anywhere. As far as I am concerned, Kotlin Multiplatform has a good prospect. Not only Google released the next generation UI development framework Jetpack Compose on Google IO 2019, but Apple also brought us SwiftUI on WWDC 2019, which means that if someone unifies the APIs of these two frameworks, we can use Kotlin to write cross-platform code with native performance. The Demo of this article has been uploaded to github, you can clone and study it if you are interested (although the code is very poor). Feel free to raise issue if you have any questions. Have Fun!
Thank you so much for reading this article. I’m so sorry for my poor English, but I hope you can understand what I want to express.